You can get the number of rows in Pandas DataFrame using len(df.index) and df.shape[0] properties. Pandas allow us to get the shape of the DataFrame by counting the number of rows in the DataFrame.
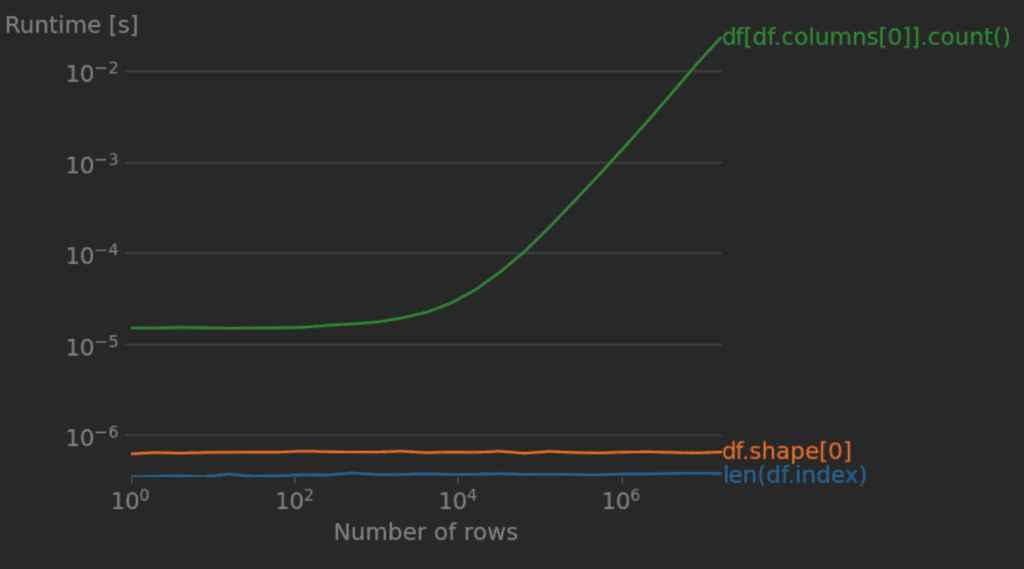
DataFrame.shape property returns the rows and columns, for rows get it from the first index which is zero; like df.shape[0] and for columns count, you can get it from df.shape[1]. Alternatively, to find the number of rows that exist in a DataFrame, you can use DataFrame.count() method, but this is not recommended approach due to performance issues.
In this article, I will explain how to count or find the DataFrame rows count with examples.
Key Points –
- The
shapeattribute returns a tuple of the form(rows, columns), where the first element represents the number of rows. - The
len()function can be used to return the number of rows in a DataFrame. - Accessing the first element of the
shapetuple gives the number of rows directly. - Accessing
shape[0]is more efficient than usinglen()becauseshapeis a direct attribute of the DataFrame. - Accessing the first element of the
shapetuple gives the number of rows directly. - When applying filters or conditions, the number of rows can change, and you can use these methods to get the updated count.
1. Quick Examples of Get the Number of Rows in DataFrame
If you are in hurry, below are some quick examples of how to get the number of rows (row count) in Pandas DataFrame.
# Quick examples of get the number of rows
# Example 1: Get the row count
# Using len(df.index)
rows_count = len(df.index)
# Example 2: Get count of rows
# Using len(df.axes[])
rows_count = len(df.axes[0])
# Example 3:Get count of rows
# Using df.shape[0]
rows_count = df.shape[0]
# Example 4: Get count of rows
# Using count()
rows_count = df.count()[0]
If you are a Pandas learner, read through the article as I have explained these examples with the sample data to understand better.
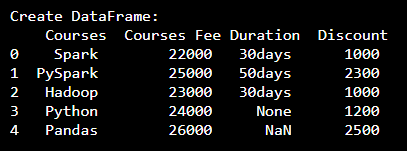
Let’s create a Pandas DataFrame with a dictionary of lists, pandas DataFrame columns names Courses, Fee, Duration, Discount.
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
technologies= {
'Courses':["Spark","PySpark","Hadoop","Python","Pandas"],
'Courses Fee' :[22000,25000,23000,24000,26000],
'Duration':['30days','50days','30days', None,np.nan],
'Discount':[1000,2300,1000,1200,2500]
}
df = pd.DataFrame(technologies)
print("Create DataFrame:\n", df)
Yields below output.
2. Get Number of Rows in DataFrame
You can use len(df.index) to find the number of rows in pandas DataFrame, df.index returns RangeIndex(start=0, stop=8, step=1) and use it on len() to get the count. You can also use len(df) but this performs slower when compared with len(df.index) since it has one less function call. Both these are faster than df.shape[0] to get the count.
If performance is not a constraint better use len(df) as this is neat and easy to read.
# Get the row count using len(df.index)
print(df.index)
# Outputs:
# RangeIndex(start=0, stop=5, step=1)
print('Row count is:', len(df.index))
print('Row count is:', len(df))
# Outputs:
# Row count is:5
3. Get Row Count in DataFrame Using .len(DataFrame.axes[0]) Method
Pandas also provide Dataframe.axes property that returns a tuple of your DataFrame axes for rows and columns. Access the axes[0] and call len(df.axes[0]) to return the number of rows. For columns count, use df.axes[1]. For example: len(df.axes[1]).
Here, DataFrame.axes[0] returns the row axis (index), and len() is then used to get the length of that axis, which corresponds to the number of rows in the DataFrame.
# Get the row count using len(df.axes[0])
print(df.axes)
# Output:
# [RangeIndex(start=0, stop=5, step=1), Index(['Courses', 'Courses Fee', 'Duration', 'Discount'], dtype='object')]
print(df.axes[0])
# Output:
# RangeIndex(start=0, stop=5, step=1)
print('Row count is:', len(df.axes[0]))
# Outputs:
# Row count is:5
4. Using df.shape[0] to Get Rows Count
Pandas DataFrame.shape returns the count of rows and columns, df.shape[0] is used to get the number of rows. Use df.shape[1] to get the column count.
In the below example, df.shape returns a tuple containing the number of rows and columns in the DataFrame, and df.shape[0] specifically extracts the number of rows. This approach is concise and widely used for obtaining the row count in Pandas DataFrames.
# Get row count using df.shape[0]
df = pd.DataFrame(technologies)
row_count = df.shape[0] # Returns number of rows
col_count = df.shape[1] # Returns number of columns
print(row_count)
# Outputs:
# Number of rows: 5
5. Using df.count() Method
This is not recommended approach due to its performance but, still I need to cover this as this is also one of the approaches to get the row count of a DataFrame. Note that this ignores the values from columns that have None or Nan while calculating the count. As you see, my DataFrame contains 2 None/nan values in column Duration hence it returned 3 instead of 5 on the below example.
# Get count of each column
print(df.count())
# Outputs:
# Courses 5
# Courses Fee 5
# Duration 3
# Discount 5
# dtype: int64
Now let’s see how to get the row count.
# Get count of rows using count()
rows_count = df.count()[0]
rows_count = = df[df.columns[0]].count()
print('Number of Rows count is:', rows_count )
# Outputs:
# Number of Rows count is: 5
