Introduction to ttk elements
So far, you have learned that a theme is a collection of styles that defines the appearance of all Tkinter widgets.
A style is a description of the appearance of a widget class. A style is composed of one or more elements.
For example, a Label consists of border, padding and label elements. And these elements are nested within each other like the following picture:
In general, most of the built-in ttk styles use the concept of a layout to organize the different element layers that build up a widget.
To get the layout of a widget class, you use the layout() method of the Style object like this:
style.layout(widget_class)Code language: Python (python)If a widget class doesn’t have a layout, the layout() method will raise a tk.TclError exception.
The layout() method returns a list of tuples (element_name, description), where:
element_nameis the name of the element.descriptionis a dictionary that describes the element.
The following example uses the layout() method to get the layout of the TLabel widget class:
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
class App(tk.Tk):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
style = ttk.Style(self)
layout = style.layout('TLabel')
print(layout)
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = App()
app.mainloop()Code language: Python (python)The following output shows the style’s layout of the TLabel:
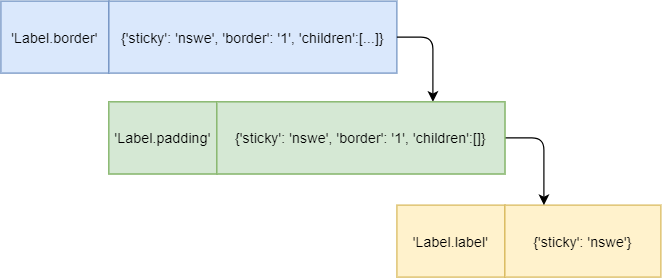
[('Label.border',
{'sticky': 'nswe',
'border': '1',
'children': [('Label.padding',
{'sticky': 'nswe',
'border': '1',
'children': [('Label.label',
{'sticky': 'nswe'})]
})]
}
)]Code language: Python (python)The TLabel has three elements nested within each other:
- The
Label.borderis the outermost element that has thesticky,border, andchildrenkeys. - The
Label.paddingis nested inside theLabel.border. It also has thesticky,border, andchildrenkeys. - The
Label.labelis the innermost element that has only onestickykey.
For example, when an element has a sticky key with the value of nswe, it would be stretched to adhere to the north, south, west, and east of the parent element.
Note that the style’s layout of a widget’s class depends on the current theme. If you change the theme, the layout may be different.
Element options
Each element has a list of options that specify the appearance of the element. To get the list of option names, you use the element_options() method of Style object:
style.element_options(styleName)Code language: Python (python)The following program shows the element options of the Label.border, Label.padding, and Label.label elements:
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
class App(tk.Tk):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
style = ttk.Style(self)
# layout
layout = style.layout('TLabel')
print(layout)
# element options
print(style.element_options('Label.border'))
print(style.element_options('Label.padding'))
print(style.element_options('Label.label'))
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = App()
app.mainloop()Code language: Python (python)Output:
('relief',)
('padding', 'relief', 'shiftrelief')
('compound', 'space', 'text', 'font', 'foreground', 'underline', 'width', 'anchor', 'justify', 'wraplength', 'embossed', 'image', 'stipple', 'background')Code language: Python (python)In this output:
- The
Label.borderelement has one option:'relief'. - The
Label.paddingelement has three options:'padding','relief', and'shiftrelief'. - The
Label.labelelement has many options including'font','foreground','with', etc.
Attributes of element options
To get a list of attributes associated with an element option, you use the lookup() method of the Style object:
style.lookup(layout_name, option_name)Code language: Python (python)The following example shows the attributes of the font, foreground, and background options in the TLabel.label element:
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
class App(tk.Tk):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
style = ttk.Style(self)
# attributes of the font, foreground, and background
# of the Label.label element
print(style.lookup('Label.label', 'font'))
print(style.lookup('Label.label', 'foreground'))
print(style.lookup('Label.label', 'background'))
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = App()
app.mainloop()Code language: Python (python)Output:
TkDefaultFont
SystemWindowText
SystemButtonFaceCode language: Python (python)As you can see clearly from the output, the font is TkDefaultFont, the foreground is SystemWindowText, and the background is SystemButtonFace.
Put it all together
The following shows how to change the appearance of a Label widget:
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
class App(tk.Tk):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.geometry('500x100')
message = 'This is an error message!'
label = ttk.Label(self, text=message, style='Error.TLabel')
label.pack(expand=True)
style = ttk.Style(self)
style.configure('Error.TLabel', foreground='white')
style.configure('Error.TLabel', background='red')
style.configure('Error.TLabel', font=('Helvetica', 12))
style.configure('Error.TLabel', padding=(10, 10))
if __name__ == "__main__":
app = App()
app.mainloop()Code language: Python (python)Summary
- A ttk widget is made up of elements. The
layoutdetermines how elements assembled the widget. - Use the
Style.layout()method to retrieve the layout of a widget class. - Use the
Style.element_options()method to get the element options of an element. - Use the
Style.lookup()method to get the attributes of an element option.
